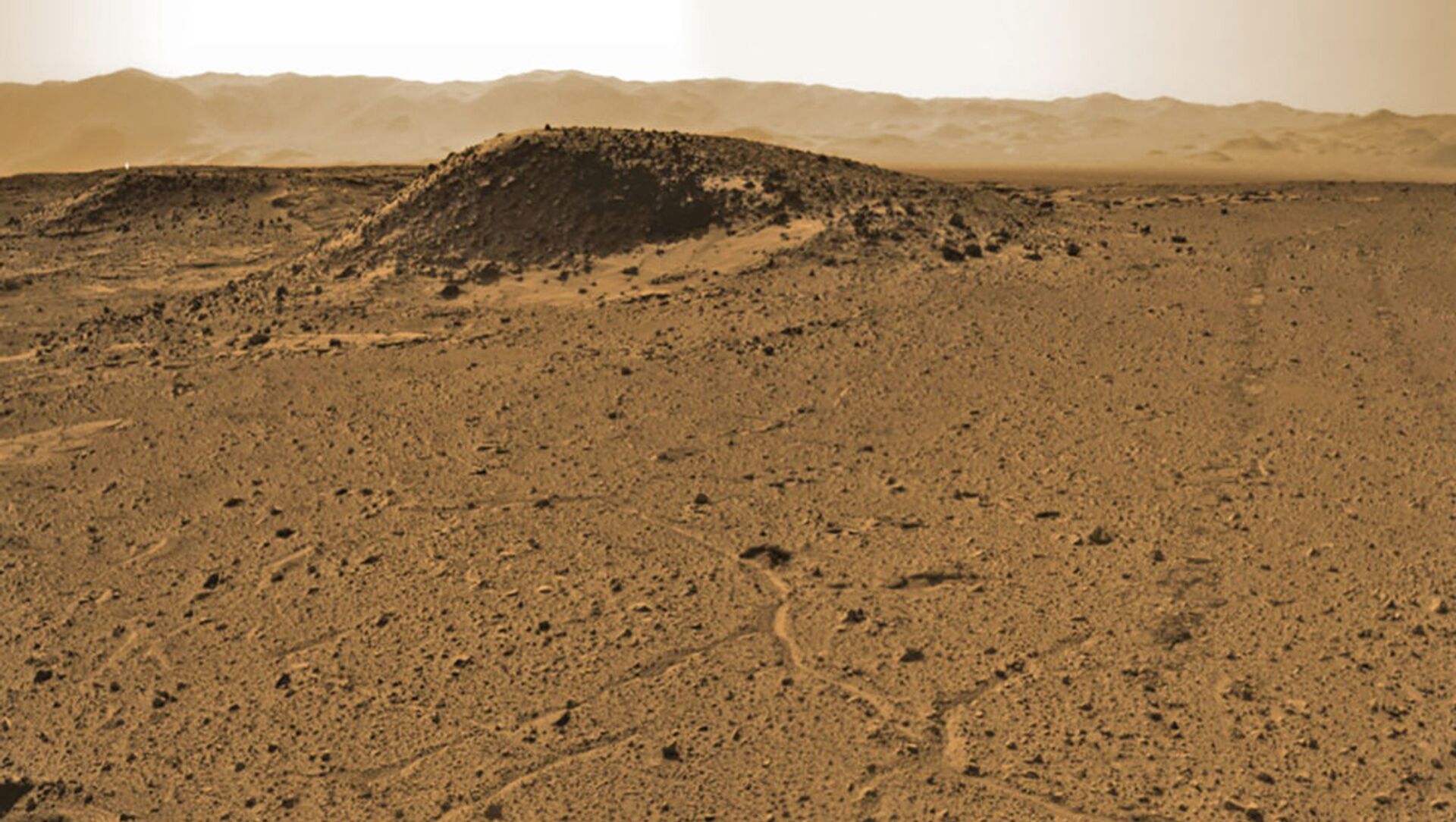
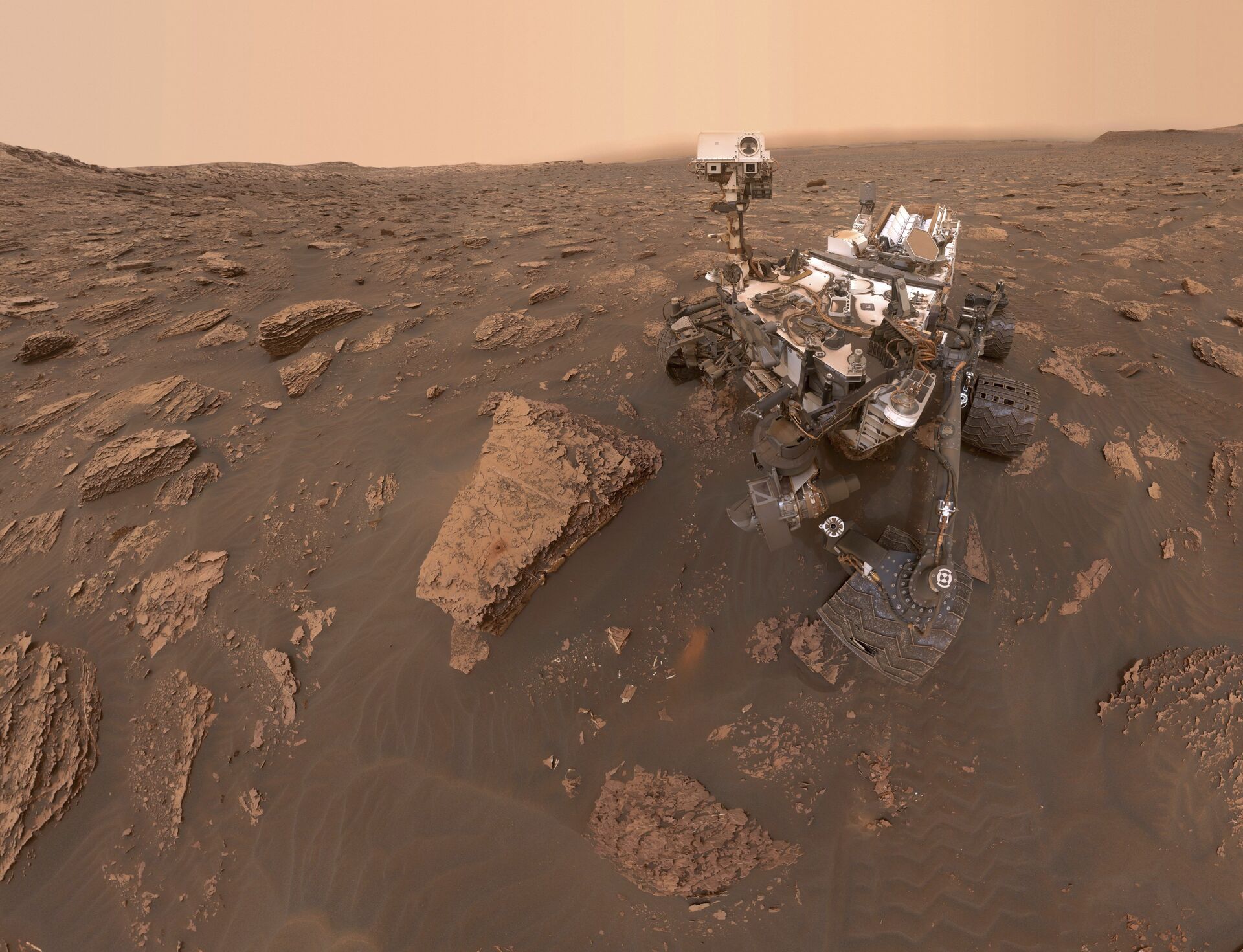
Lengthy dry periods alternated with wetter stints seem to have occurred several times on Mars before the rocky Red Planet turned into the utterly desiccated wilderness as we know it today, a study claims citing analysed data from the NASA Curiosity rover. The findings have been published in the journal Geology.
Using the ChemCam instrument and a telescope on the vehicle, which is currently combing the base of Aeolis Mons - a mountain in the centre of the Gale crater - researchers managed to study the build-up of sedimentary beds scattered around the planet’s surface.
Moving up through the red terrain, made of several hundred feet of thick dust, the types of beds change their composition drastically, the research group came to believe.
More specifically, dunes at the top of the huge masses of clay that form the foot of Mount Sharp mean that those structures migrated at some point, having been carried by the winds.
The dunes probably gained their present shape during a long dry stint, the researchers noted, and higher up they found thin brittle and resistant beds, which were deemed typical of river floodplain deposits.
These features hint at the return of wetter weather at some point, perhaps the result of flooding inside the Gale crater.
There had been several such changes in the landscape until today’s overwhelmingly arid conditions settled in about three billion years ago, at a time when the Earth consisted mostly of water.
During its mission on Mars, which has been continuing since 2012, Curiosity is expected to continue climbing the foothills of Mount Sharp and further drill into different types of beds to understand better the geological composition of the scorched Martian land, and test the afore-mentioned theory.
Those shifts give an idea of how the ancient climate could have evolved, and the rover’s follow-up work would potentially shed light on their origins, the team stated.




