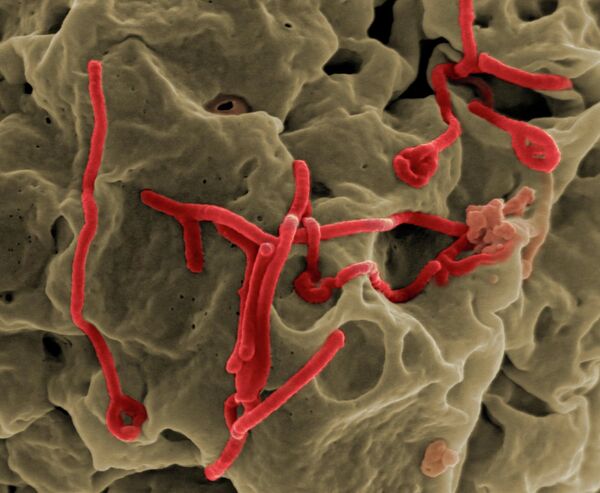
MOSCOW, October 10 (RIA Novosti) - The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified some 146 contacts in Uganda, which are currently being monitored for signs and symptoms of Marburg virus disease (MVD), the organization reported on Friday.
"As of today, a total of 146 contacts have been identified and are being monitored for signs and symptoms compatible with MVD. Eleven of the contacts developed signs and symptoms compatible with Marburg virus disease. All samples from symptomatic contacts have tested negative so far. Second samples have been taken from them and are being tested at the Uganda Virus Research Institute (UVRI)," the organization said on its official website concerning the spread of the disease in Uganda.
WHO along with Doctors Without Borders (MSF) and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) are supporting the Ministry of Health of Uganda's (MoH) National Task Force against the severe virus. According to WHO, four multi-disciplinary teams have been deployed in the country to carry out a risk assessment. Surveillance, contact tracing, and follow-up activities are being implemented in Kampala, Mpigi and Kasese.
On October 5 the MoH informed WHO of a confirmed case of the virus in Kampala, Uganda. The case involved a healthcare worker who was infected with the disease on September 11 and died September 28 after suffering common symptoms of the disease including fever, headache, abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea. The individual had no history of traveling outside of Mpigi or contact with any person possibly infected with the illness. The healthcare worker also had not eaten bush meat or been in contact with bats in the last four weeks.
MVD is a deadly virus similar to the Ebola virus, which is currently plaguing countries in West Africa. Human infection of the Marburg disease can be caused by prolonged exposure to mines or caves inhabited by bat colonies while transmission is attributed to human-to-human contact via blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids from individuals infected with the disease. Case fatality rates in MVD outbreaks have ranged from 24 percent to 88 percent. The latest outbreak of MVD in Uganda affected the Kabale District, Kampala, Ibanda, Mbarara and Kabarole in 2012 resulting in 20 cases, 9 of which were fatal. There is currently no specific antiviral treatment or vaccine against the illness.