<!-- /* Font Definitions */ @font-face {font-family:SimSun; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-alt:ЛОМе; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:3 135135232 16 0 262145 0;} @font-face {font-family:"\@SimSun"; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:3 135135232 16 0 262145 0;} /* Style Definitions */ p.MsoNormal, li.MsoNormal, div.MsoNormal {mso-style-parent:""; margin:0cm; margin-bottom:.0001pt; mso-pagination:widow-orphan; font-size:12.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-fareast-language:RU;} p.MsoBodyText, li.MsoBodyText, div.MsoBodyText {margin:0cm; margin-bottom:.0001pt; text-align:justify; text-justify:inter-ideograph; mso-pagination:widow-orphan; font-size:14.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-ansi-language:EN-US; mso-fareast-language:RU;} @page Section1 {size:612.0pt 792.0pt; margin:2.0cm 42.5pt 2.0cm 3.0cm; mso-header-margin:36.0pt; mso-footer-margin:36.0pt; mso-paper-source:0;} div.Section1 {page:Section1;} --> The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) - the world’s largest particle accelerator, which was developed by physicists from all over the world – is again being readied for start-up, a year after an accident put it out of order.

The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) - the world’s largest particle accelerator, which was developed by physicists from all over the world – is again being readied for start-up, a year after an accident put it out of order.
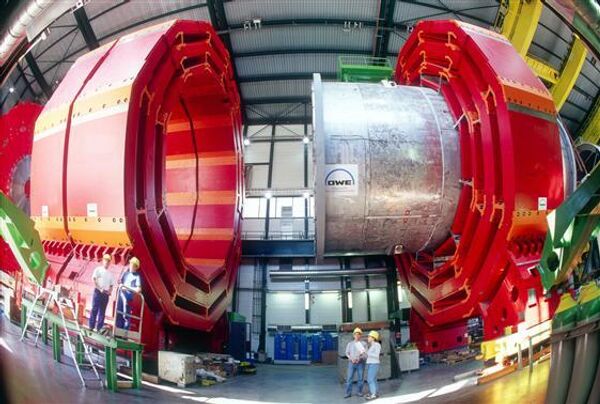

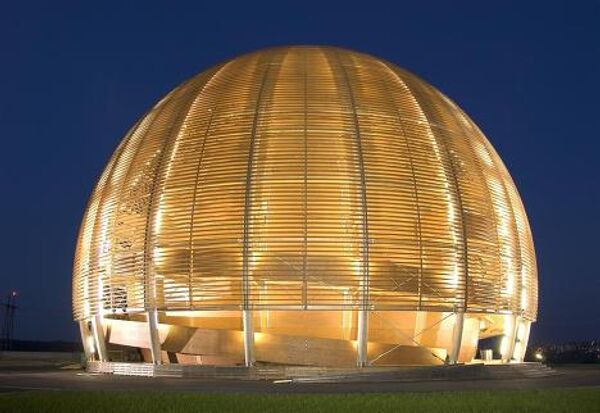
The Large Hadron Collider, built by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) with the help of several thousand scientists from 85 countries, accelerates protons to an energy of 7 teraelectron-Volts (TeV).
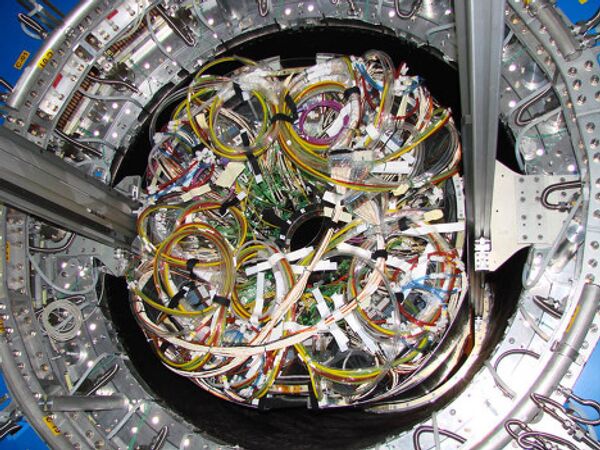
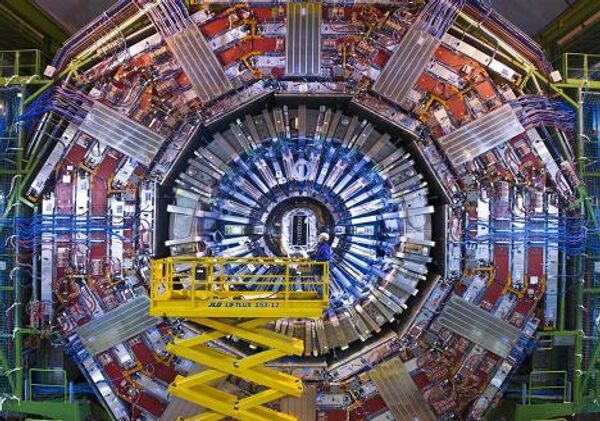
At four points along the collider ring, bunches of protons will collide to generate a multitude of particles and radiation to be registered by means of detectors.

Two of these – ATLAS and CMS – are general-purpose devices, while the other two, ALICE and LHCb, are specialized.
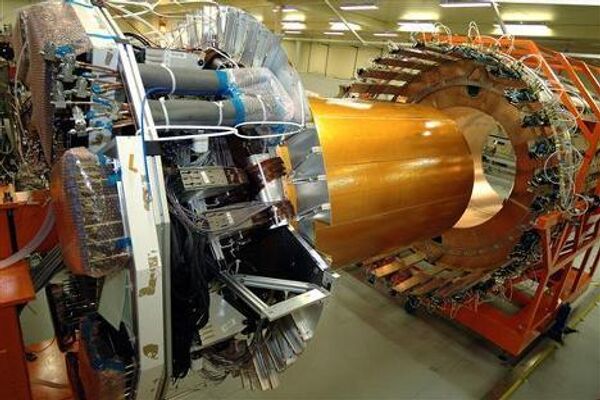

ATLAS is the largest such detector in history.
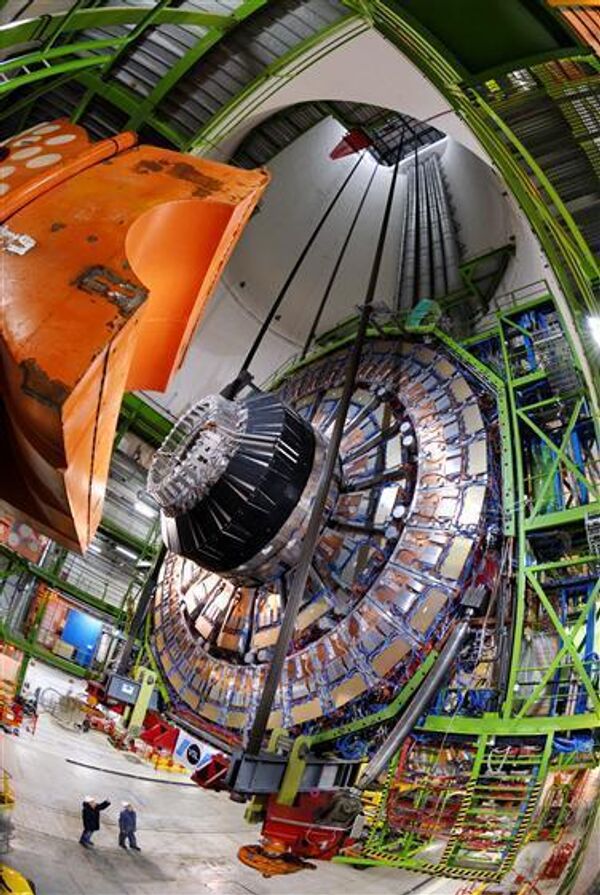

In tandem with CMS it can help researchers to detect traces of the Higgs boson, a hypothesized particle that, according to the current theories, explains the existence of mass in elementary particles. Searching for this particle is considered one of the central tasks of the whole project.

The detector ALICE is expected to record another experiment – that involving collisions of lead nuclei accelerated on the collider.

These collisions, scientists believe, will help them to learn more about the so-called quark-gluon plasma – the state of matter immediately after the Big Bang.

LHCb is necessary to study asymmetry between matter and anti-matter by examining interactions between particles containing so-called b-quarks.

The scientists hope to come up with an answer to the question “Why there is no anti-matter in the observable universe?”
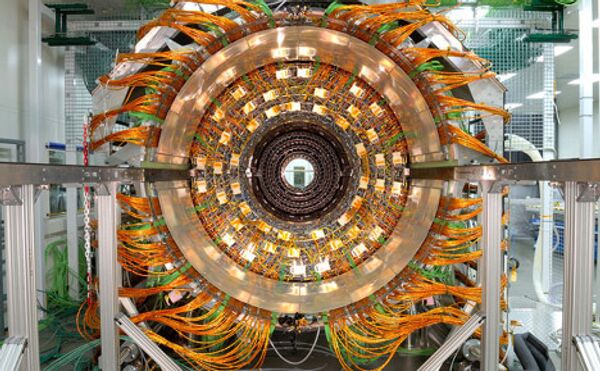
The idea of building the LHC was first conceived in 1984. But official approval did not follow until 10 years later.
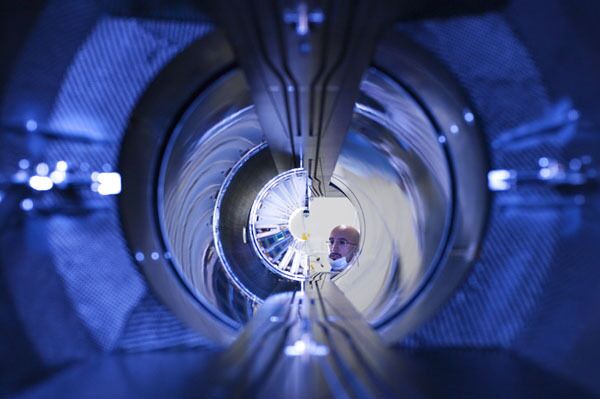
The construction of the LHC started in 2001, when another accelerator – the Large Electron-Positron Collider (LEPC) – completed its operation.
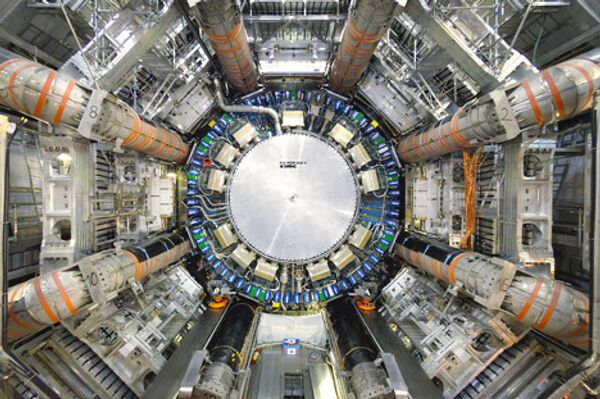
In the fall of 2008, the Large Hadron Collider was shut down because of an accident a few days after launch.

A defective high-resistance electrical contact caused the magnets to lose their superconducting properties and the cooling system to break down.

Several tons of liquid helium were released into the collider tunnel, deforming the pipes of the cooling system and the channels where particles were circulating.

Repair and upgrade work took more than a year.



